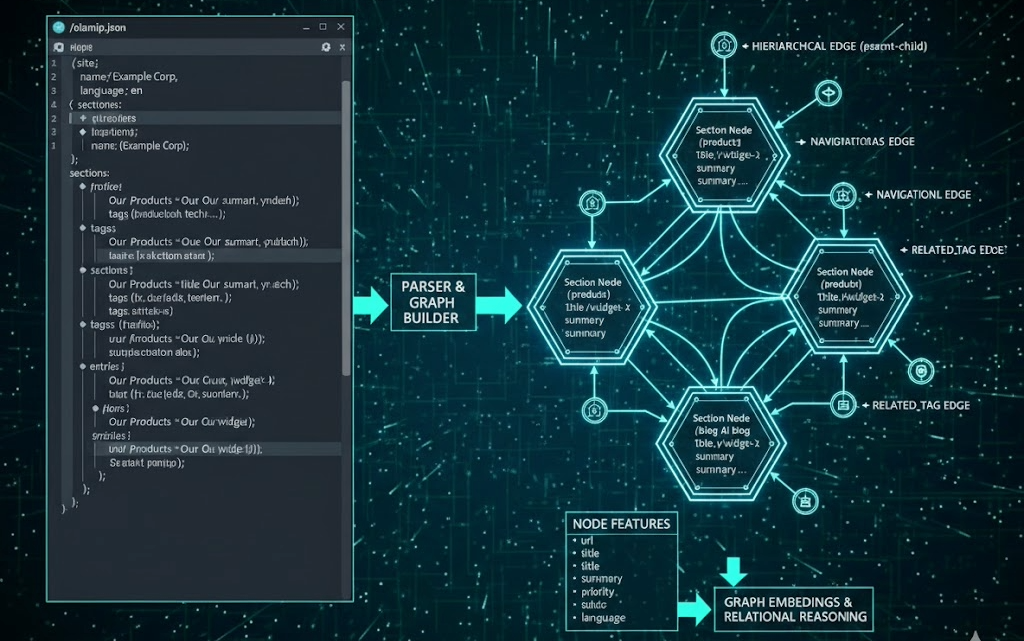
As AI becomes the primary interface for discovering and interpreting online content, the web is shifting from a browser-first medium to an AI-first knowledge ecosystem. To move beyond the limitations of noisy, layout-driven HTML, a new architecture is emerging: the combination of DeepMind’s Graph Nets and the OLAMIP standard.
By pairing a neural architecture designed for relational reasoning with a structured semantic protocol, we can transform websites from visual documents into high-fidelity knowledge graphs.
The Architecture of Understanding
To understand this synergy, we must look at the two components as a single machine:
- Graph Nets provide the computational structure. They are a family of neural networks that reason over “graphs” (entities and their relationships).
- OLAMIP provides the semantic content. As an open standard (via
/olamip.json), it offers human-curated summaries, metadata, and explicit site hierarchies.
In this partnership, OLAMIP acts as the ground truth, and Graph Nets act as the reasoning engine.
Strategic Synergies: Why They Excel Together
1. Structural Alignment: Hierarchy as a Blueprint
Graph Nets require an organizational blueprint to function. OLAMIP provides this explicitly through its hierarchical sections and subsections.
- Nodes: Graph Nets treat OLAMIP sections and entries as individual nodes.
- Edges: The links between these sections—defined by OLAMIP’s structure—become the edges that dictate how information flows.
- Anchors: By using OLAMIP’s canonical URLs as stable node identifiers, the graph remains consistent even if the website’s visual design changes.
2. Message Passing and Deep Context
Graph Nets use a process called “message passing” to propagate information across the network. Because OLAMIP provides clean, human-curated summaries for every node, the Graph Net can efficiently share context between siblings, parents, and children. This allows an AI to understand that a specific “Sub-entry” carries the weight and topical authority of its “Parent Section.”
3. High-Signal Retrieval (RAG)
When integrated into a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline, this combination eliminates the “lost in the middle” problem common in LLMs.
- Metadata Integration: Graph Nets incorporate OLAMIP’s tags, priority signals, and content types as node attributes.
- Relational Search: Instead of searching for keywords, the AI searches for semantic clusters. It can retrieve a primary summary from OLAMIP while simultaneously understanding its relational context through the Graph Net.
Comparative Analysis
Table 1: How They Complement Each Other
| Capability | Graph Nets (The Engine) | OLAMIP (The Fuel) | Combined Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchy | Processes relational data | Declares structural order | High-fidelity site mapping |
| Priority | Weights node importance | Provides explicit signals | Optimized sampling for training |
| Context | Propagates via edges | Defines via summaries | Deep, multi-step reasoning |
| Updates | Supports incremental growth | Offers delta updates | Real-time, efficient refresh |
Table 2: AI Pipeline Integration
| Pipeline Stage | Graph Nets Contribution | OLAMIP Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Ingestion | Builds the relational graph | Supplies clean, structured text |
| Embedding | Calculates relational context | Ensures semantic clarity |
| Retrieval | Identifies relevant clusters | Provides metadata-rich entries |
| Learning | Enables structured reasoning | Supplies multilingual, curated text |
The combination of DeepMind’s Graph Nets and OLAMIP represents a departure from the “brute force” scraping of the past. It offers a sophisticated, low-noise pipeline where websites are treated as structured intelligence rather than flat text.
By giving AI both the structure to reason and the content to interpret, creators can ensure their digital assets are understood with the clarity and intent they originally designed.